Understanding the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps is essential for engineers, technicians, and industry professionals who rely on efficient fluid handling systems. Pumps are vital components in a wide range of applications—from water treatment and agriculture to chemical processing and HVAC systems. However, not all pumps are created equal. Knowing the distinctions between vertical pumps and centrifugal pumps can significantly impact your choice of equipment, installation process, and overall system performance.
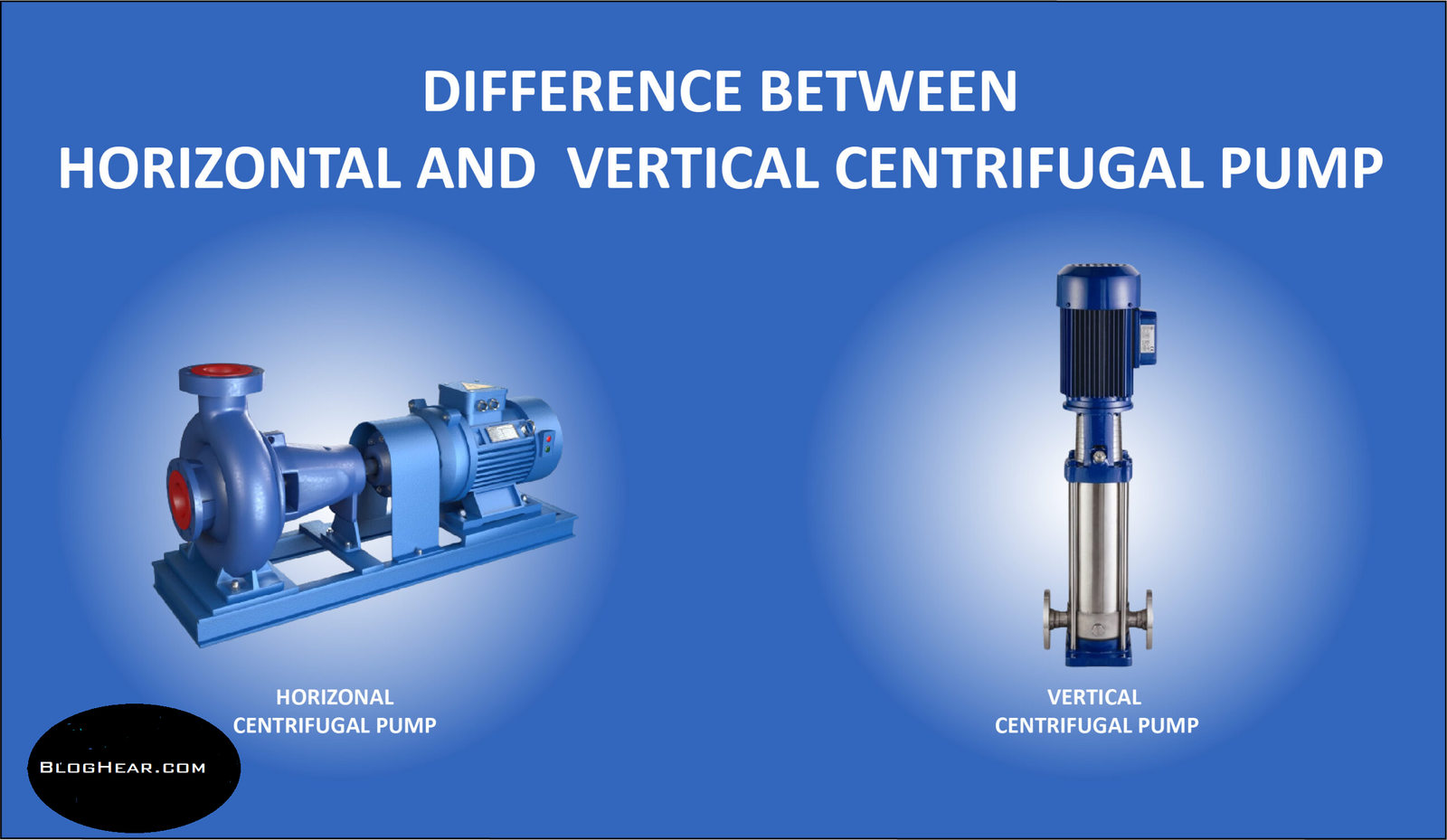
The difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps mainly lies in their design, orientation, and application. Vertical pumps feature a vertical shaft with the motor positioned above ground, making them ideal for deep well pumping and spaces with limited floor area. Centrifugal pumps, on the other hand, usually have a horizontal shaft and are widely used for transferring fluids near the surface in many industrial settings. Each type has unique advantages and limitations depending on the specific requirements of your operation.
In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps, covering their design features, performance, maintenance, and best use cases. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which pump type suits your needs and why this distinction matters for maximizing efficiency and reliability.
What Are Vertical Pumps?
Vertical pumps are a type of centrifugal pump where the motor is mounted above the pump casing, and the impeller sits vertically submerged in the fluid source, often in a well or sump. These pumps are specifically designed for applications where the fluid source is deep or where floor space is limited. Vertical pumps are sometimes referred to as vertical turbine pumps because of their unique construction and turbine-style impellers.
What Are Centrifugal Pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are one of the most common pump types used globally. They work by converting rotational kinetic energy, typically from an electric motor or engine, into hydrodynamic energy to move fluids. The impeller spins and throws fluid outward through centrifugal force, increasing the fluid’s velocity and pressure. Centrifugal pumps come in many configurations, including horizontal and vertical orientations.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Centrifugal Pumps
1. Orientation and Design
The primary difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps lies in their physical orientation. Vertical pumps have a vertically aligned shaft and impeller, with the motor placed above ground and the impeller submerged in the fluid. In contrast, centrifugal pumps usually feature a horizontal shaft orientation, with the motor and pump aligned on the same horizontal plane.
This design difference significantly impacts the installation space required and the types of applications suited for each pump.
2. Space and Footprint
Vertical pumps are favored when there is limited floor space or when pumping fluids from deep wells or sumps. Their vertical design means the footprint on the ground is minimal. Conversely, centrifugal pumps with horizontal shafts require more horizontal space but are easier to access for maintenance due to their layout.
3. Applications
Understanding the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps also involves recognizing where each excels:
- Vertical pumps are ideal for deep well pumping, sump dewatering, and applications requiring fluid lifting from underground or confined spaces. They are commonly used in municipal water supply, irrigation, and cooling towers.
- Centrifugal pumps are widely used in industries where high flow rates at moderate pressures are needed, such as HVAC systems, chemical processing, and wastewater management.
4. Maintenance and Accessibility
Maintenance accessibility is another key difference. Vertical pumps often have motor and bearings located above ground, making it easier to service without disturbing the submerged components. However, accessing the impeller requires lowering parts into the well or sump.
Horizontal centrifugal pumps usually allow easier direct access to both the impeller and motor but take up more space during servicing.
5. Performance Characteristics
While both pump types operate on centrifugal force principles, vertical pumps can handle higher suction lifts due to their submersible impeller design. This makes vertical pumps more suitable for lifting fluids from deep sources. Centrifugal pumps, especially horizontal types, typically operate at lower suction heads and are used where fluid sources are at or near ground level.
6. Installation Complexity
The installation process varies with pump type. Vertical pumps require careful alignment of the vertical shaft and secure mounting of the column assembly, making installation more complex. Centrifugal pumps generally have simpler installations due to their horizontal shaft and compact design.
Advantages of Vertical Pumps
- Space-saving vertical design
- Suitable for deep well and sump applications
- Easier motor maintenance (above ground)
- Can handle large flow rates and high pressures in confined areas
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps
- Simple design and easy installation
- Wide range of sizes and capacities available
- Effective for many industrial and commercial fluid transfer needs
- Easy to maintain and repair due to accessible components
Summary: Difference Between Vertical and Centrifugal Pumps
To summarize the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps, vertical pumps excel in applications requiring deep fluid lifting and limited installation space, with a vertical orientation that optimizes footprint and motor protection. Centrifugal pumps, meanwhile, offer versatile solutions for various flow rates and pressures, with simpler horizontal designs better suited to surface-level fluid transfer.
Choosing between these two types depends largely on your specific application, space availability, fluid depth, and maintenance preferences.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps is crucial for selecting the right pump for your specific application. Each pump type offers distinct advantages: vertical pumps excel in deep well and space-constrained environments, while centrifugal pumps provide versatile, efficient solutions for surface-level fluid transfer. By carefully evaluating factors such as installation space, fluid source depth, maintenance accessibility, and performance needs, you can make an informed decision that enhances your system’s reliability and efficiency.
Both vertical and centrifugal pumps play vital roles across various industries, and knowing their differences empowers engineers and facility managers to optimize operations effectively. Whether you need a pump for irrigation, water treatment, or industrial processing, recognizing the difference between vertical and centrifugal pumps helps you match the right technology to your requirements.
For more expert insights, comprehensive reviews, and practical guides on industrial equipment and technology, visit BlogHear.com — your trusted source for the latest in tech and innovation.