How vertical pumps work is a crucial topic for professionals in industries such as water treatment, power generation, agriculture, and manufacturing. If you’ve ever wondered why vertical pumps are favored in large-scale fluid handling operations, or how they manage to deliver high-pressure performance from deep fluid sources, then this guide is exactly what you need. Understanding how vertical pumps work can help engineers, facility managers, and equipment buyers make informed decisions that lead to better efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and longer equipment life.
So, what makes vertical pumps different? Unlike horizontal pumps, vertical pumps are specifically designed to handle deep well or sump applications. Their vertical structure allows the motor to stay above ground while the impellers, located at the bottom, operate while submerged in the fluid source. This setup offers major advantages in terms of space-saving, performance, and ease of maintenance.
In this post, we will explore how vertical pumps work in detail—from their core components and operation to their industrial applications and benefits. Whether you’re researching a new installation or simply upgrading an old system, knowing how vertical pumps work will give you a solid technical foundation to make the right choices.
What Are Vertical Pumps?
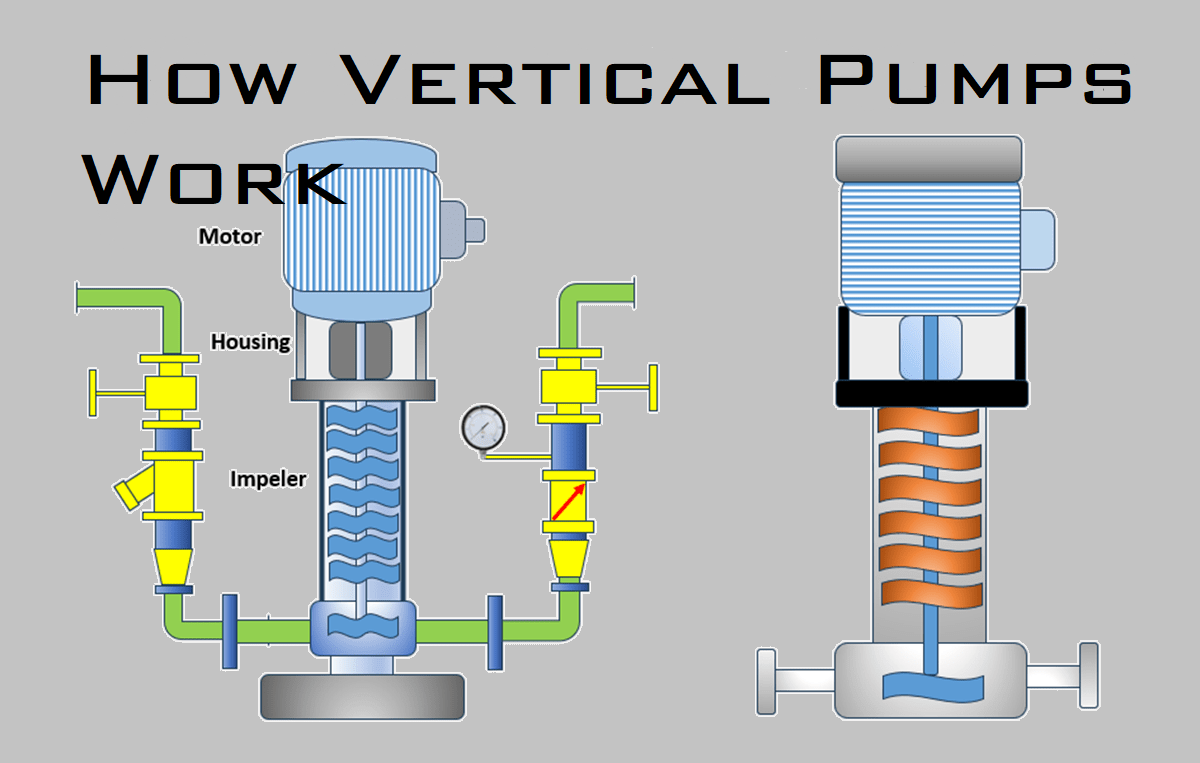
Before diving into how vertical pumps work, it’s important to define what they are. Vertical pumps, also known as vertical turbine pumps or vertical centrifugal pumps, are designed with a motor positioned above the pump and an impeller located at the bottom, submerged in the fluid source. This vertical orientation allows for a smaller footprint and is ideal for deep well or sump pumping applications.
The basic components of a vertical pump include:
- Motor (mounted above ground)
- Column pipe (transfers energy to the impeller)
- Pump bowl assembly (includes the impellers and diffusers)
- Discharge head (redirects flow from vertical to horizontal)
How Vertical Pumps Work: The Fundamentals
So, how do vertical pumps work exactly?
- Motor Activation: The process begins when the electric motor (or turbine motor) at the surface is activated.
- Energy Transmission: The motor’s rotational energy is transferred down the column shaft to the impellers at the bottom of the pump.
- Fluid Intake and Acceleration: The impellers, submerged in the fluid source, accelerate the liquid and create a low-pressure area, drawing in more fluid.
- Pressure Increase: As fluid passes through the diffuser bowls, pressure builds, allowing it to be lifted through the column pipe.
- Flow Discharge: Finally, the fluid exits the pump via the discharge head, which redirects it for further processing or distribution.
Understanding how vertical pumps work also involves recognizing the advantages of their design. Their vertical setup reduces the risk of motor flooding, especially in applications involving deep wells or flood-prone zones.
Key Benefits of Vertical Pumps
To fully understand how vertical pumps work, you should also know why they’re chosen over horizontal alternatives:
1. Space-Saving Design
The vertical configuration uses less horizontal floor space, making these pumps ideal for facilities with spatial constraints.
2. Deep Sump and Well Suitability
Because the impellers are submerged deep in the fluid, vertical pumps can lift water from much deeper sources than horizontal pumps.
3. High Efficiency at Variable Loads
Vertical pumps are highly efficient when handling fluctuating flow rates, which is common in industries like agriculture and municipal water supply.
4. Easy Maintenance
Most of the maintenance is done above ground, simplifying servicing and inspection. This makes the operational cost lower over time.
Applications Where Vertical Pumps Excel
To further reinforce how vertical pumps work, consider the variety of industries that rely on their precision and power:
- Water treatment plants – For moving large volumes of treated or untreated water.
- Power plants – Used in boiler feedwater and cooling tower applications.
- Agriculture – For irrigation and pumping water from deep wells.
- Mining – To dewater deep underground operations.
- Oil & gas – For moving crude oil, refined fuels, and chemicals.
Understanding how vertical pumps work can help engineers and facility managers choose the right type and configuration to meet specific operational needs.
Maintenance and Longevity
A key aspect of how vertical pumps work is their long operational life when properly maintained. Routine inspections include:
- Checking shaft alignment
- Inspecting impeller wear
- Monitoring bearing lubrication
- Ensuring seals are intact and leak-free
Because much of the pump is accessible from above ground, vertical pumps are considered easier and safer to maintain in many industrial setups.
Choosing the Right Vertical Pump
Understanding how vertical pumps work is just one part of the equation. Choosing the right pump requires evaluating:
- Flow rate and head pressure
- Fluid type (e.g., corrosive, abrasive, clean)
- Depth of the source
- Power requirements
- Material compatibility
Consulting with an experienced pump supplier or engineer is often the best way to ensure optimal performance and durability for your specific application.
Conclusion
Understanding how vertical pumps work is essential for anyone involved in industrial or commercial fluid handling systems. These pumps are not just a mechanical solution—they’re a strategic choice for operations that require efficiency, space optimization, and deep-well capabilities. From water treatment plants to mining operations, vertical pumps offer unmatched performance when correctly selected and maintained.
Throughout this article, we’ve covered how vertical pumps work from their internal components to the operational process and real-world applications. Their unique vertical structure, ability to handle large volumes of fluid, and above-ground maintenance accessibility make them the go-to option for engineers and facility managers worldwide.
If you’re looking for reliability, reduced operational costs, and high-performance pumping, vertical pumps deserve serious consideration. Now that you understand how vertical pumps work, you can approach your next pump selection or upgrade project with greater confidence and technical clarity.
For more industrial equipment guides, expert reviews, and technology insights, be sure to visit BlogHear.com — your trusted source for everything tech and innovation.
Difference Between Vertical and Centrifugal Pumps: What You Need to Know